In the equipment of the CPU (Central processing unit), many hardware suppliers distinguish not only in the available computing power, but also in the type of cores contained. In many performance descriptions the terms “physical”, “logical” or “virtual” cores are used. But what are the differences? In the following we will explain the fundamental differences.
What are physical cores?
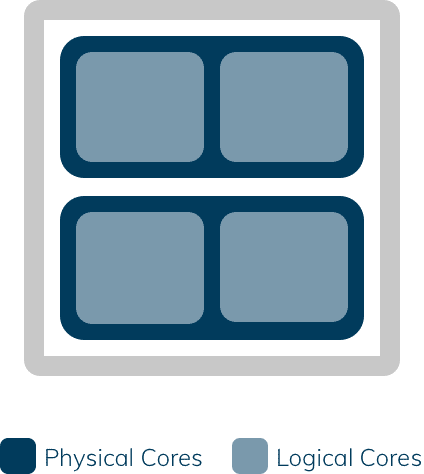
A physical core is a component of the processor and a real physical computing unit that is built into the processor and can perform all the functions of a processor. In our example there are 2 physical cores in one processor.
What are logical cores?
In order to be able to explain logical cores, we must first deal with the topic of hyper-threading.
Hyper-threading divides a physical core into two threads. A thread is an execution path within a core. The idea is to allow processes to run simultaneously and thus speed up the system because more computing tasks can be performed. A single physical core with hyper-threading appears to an operating system as two logical cores.
Thus, logical cores are understood to be the number of physical cores multiplied with the number of threads that can run on each core using hyper-threading. For example, if there are 2 physical cores with 2 threads per core, the system contains a total of 4 logical cores.
What are virtual cores?
For the description of virtual cores, we need to go even deeper into the virtualization layer.
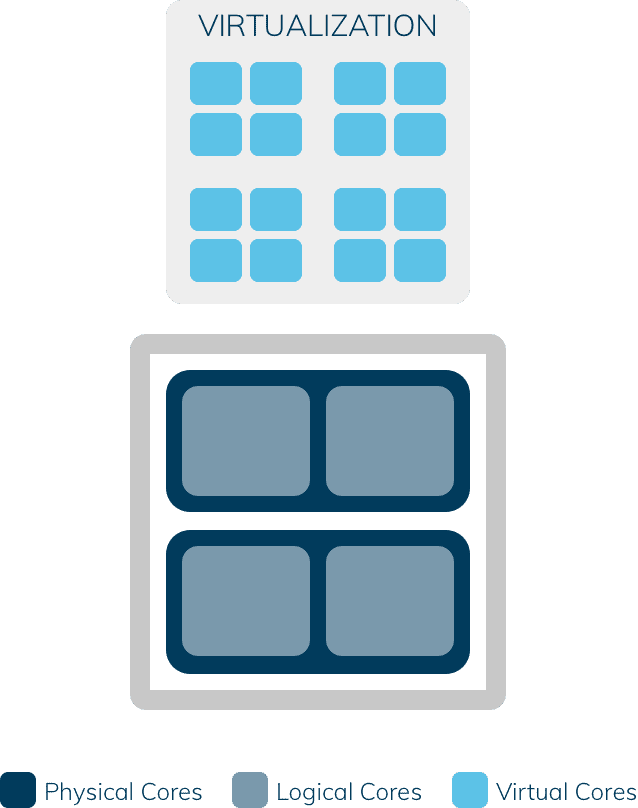
Virtual cores, also called vCores, are the number of logical cores multiplied with the CPU overbooking rate in a virtual machine. Overbooking is the division of logical cores into virtual cores. For example, an overbooking rate of 5:1 means that five vCores are assigned to a logical core. Generally, it is not possible to answer which ratio is optimal, because the workload is the decisive factor. In the meantime, however, a ratio of 4:1 has established itself as a best practice.
If the 4 logical cores mentioned in the example are overbooked 4 times, a total of 16 virtual cores are available.
Physical, logical or virtual cores: What is the best choice for me?
A virtual desktop with virtual cores is ideal for the standard user in everyday use in terms of the price/performance ratio. These are inexpensive to purchase and designed for the individual user. If several users access a multi-user environment at the same time, or if users, whether they work in a single- or multi-user environment, have high performance requirements, it is important to ensure that as many physical or logical cores as possible are available.
While our oneclick™ Virtual Desktops are equipped with virtual cores for use by a single user, the oneclick™ Virtual Desktop Infrastructure packages use dedicated physical cores with hyper-threading to provide the best possible performance for all users.
With our oneclick™ Virtual Desktops and our oneclick™ Virtual Desktop Infrastructure, you get a powerful infrastructure that you can access from anywhere via your browser and the oneclick™ platform. Depending on your performance requirements, you can choose from various packages ranging from the small single-user entry-level model to the high-performance multi-user environment.